
A list of astronomical events that took place in 2022:
Astronomical events
- January 1: The Quadrantids meteor shower peaked on this day. The Quadrantids are known for producing bright, fast-moving meteors, and this shower is known for having a sharp peak, with the greatest number of meteors occurring in just a few hours.
- January 22: A total lunar eclipse occurred on this day, and was visible from North and South America, Europe, Africa, and western Asia. During a total lunar eclipse, the Moon passes through the Earth’s shadow, and the Moon’s surface appears to turn red or orange. This is due to the way sunlight is refracted, or bent, as it passes through the Earth’s atmosphere.
- April 4: Another total lunar eclipse occurred on this day, and was visible from the same regions as the January eclipse.
- April 22: The Lyrids meteor shower peaked on this day. The Lyrids are known for producing bright, fast-moving meteors, and this shower typically produces around 20 meteors per hour at its peak.
- May 26: An annular solar eclipse occurred on this day, and was visible from parts of Canada, Greenland, and Russia. During an annular solar eclipse, the Moon passes in front of the Sun, but does not completely block it out. This results in a “ring of fire” appearance around the Moon.
- June 10: A partial lunar eclipse occurred on this day, and was visible from North and South America, Europe, Africa, and western Asia. During a partial lunar eclipse, only a portion of the Moon passes through the Earth’s shadow.
- July 20: The Delta Aquariids meteor shower peaked on this day. The Delta Aquariids are known for producing relatively faint meteors, and this shower typically produces around 15-20 meteors per hour at its peak.
- August 11: A partial solar eclipse occurred on this day, and was visible from parts of Europe, Asia, and North and South America.
- October 21: The Orionids meteor shower peaked on this day. The Orionids are known for producing relatively fast-moving and bright meteors, and this shower typically produces around 20 meteors per hour at its peak.
- November 4: Another total lunar eclipse occurred on this day, and was visible from North and South America, Europe, Africa, and western Asia.
These are just some of the notable celestial events that took place in 2022. There were likely many other interesting events that occurred throughout the year, such as planetary conjunctions, comets, and other celestial phenomena.

Astronomical Definition & Meaning
What is an astronomical object?
An astronomical object is any object in outer space that can be observed from the Earth or from other celestial objects. This includes objects such as stars, planets, moons, asteroids, comets, and other celestial bodies, as well as celestial phenomena such as meteor showers, galaxy clusters, and nebulae. Astronomical objects are often studied by astronomers, who use telescopes, satellites, and other instruments to observe and analyze them. Astronomical objects are often classified based on their characteristics, such as size, composition, temperature, and distance from the Earth. Some examples of astronomical objects include the Sun, the Moon, the planets in our solar system, and other objects in the Milky Way galaxy and beyond.
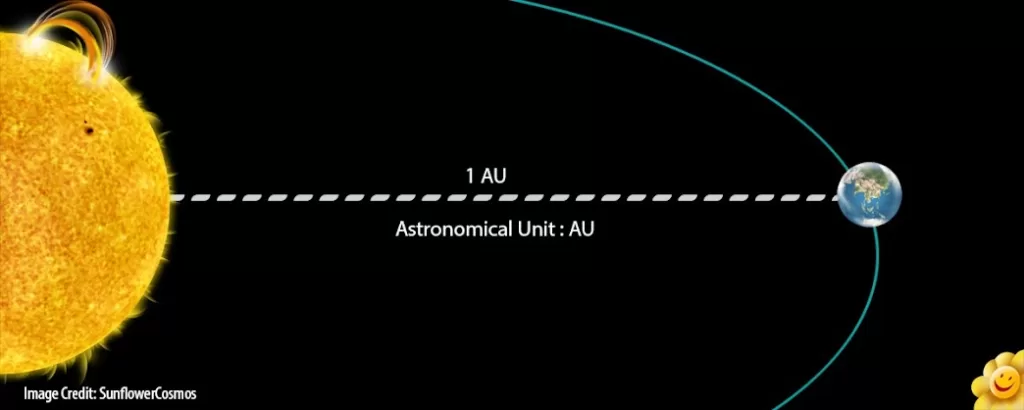
What are astronomical units?
What are astronomical units?
An astronomical unit (AU) is a unit of length that is used to measure distances within the solar system. It is defined as the average distance from the Earth to the Sun, which is about 93 million miles (149.6 million kilometers). The astronomical unit is a convenient unit to use when discussing distances within the solar system because it is similar in scale to the distances between the celestial objects in the solar system. For example, the distance from the Earth to the Moon is about 1.3 million kilometers, which is about 0.0025 AU. The distance from the Earth to Mars is about 225 million kilometers, which is about 2.5 AU. The distance from the Sun to Pluto is about 5.9 billion kilometers, which is about 39.5 AU.

What is an astronomical object?
What is the difference between astronomical body and celestial object?
The terms “astronomical body” and “celestial object” are often used interchangeably to refer to objects in outer space, such as planets, stars, moons, and other objects that can be observed from the Earth or from other celestial objects.
An astronomical body is a celestial object that is held together by its own gravity and has a round or nearly round shape. This includes objects such as stars, planets, and moons.
A celestial object is any object in outer space that can be observed from the Earth or from other celestial objects. This includes not only astronomical bodies, but also other objects such as asteroids, comets, and celestial phenomena like meteor showers, galaxy clusters, and nebulae.
So, all astronomical bodies are celestial objects, but not all celestial objects are astronomical bodies.
What is distance in astronomy?
Distance is an important concept in astronomy, as celestial objects can be very far away from each other and from the Earth. In astronomy, distance is often used to describe the separation between two celestial objects or between the Earth and a celestial object.
There are many different units that are used to measure distance in astronomy, including the astronomical unit (AU), light-year, parsec, and others. The choice of unit often depends on the scale of the distances being measured. For example, the astronomical unit is commonly used to measure distances within the solar system, while light-years and parsecs are used to measure distances between stars and galaxies.
Distance is also a key factor in understanding the properties and characteristics of celestial objects. For example, the distance of a celestial object from the Earth can affect its apparent size and brightness, and can also provide clues about its age, temperature, and other properties.
